
—From high-efficiency compressors to intelligent control, analyzing the key role of Hall current sensors in air conditioning systems
In China, air conditioning has become a necessity in households, with almost every room equipped with one. Statistics show that the Chinese air conditioning market will exceed 800 billion yuan in 2025. As people's living standards continue to improve, their demands for air conditioning are also increasing, requiring both energy efficiency and intelligent features.
The 2025 China Household Appliance Technology Conference was held in Hefei, Anhui Province on November 13th. At the air conditioning forum, experts and scholars from major air conditioning brands and universities shared their insights on 11 core topics, including dynamic energy efficiency, energy-saving technologies, intelligent control, and material and structural innovation, showcasing the latest achievements and future directions of technological innovation in the air conditioning industry. For example, the Changhong air conditioning team used AI algorithms to accurately identify refrigerant content, overcoming the industry pain points of low efficiency and large errors in traditional detection methods. Technological upgrades have become the core driving force for industry development. However, air conditioning systems also face severe technical challenges in achieving energy efficiency, intelligence, and the application of new refrigerants. CHIPSENSE current sensor has made changes to address this issue.
For instance, if the new national standard requires air conditioning energy efficiency to be upgraded to Level 1, the current monitoring scheme lacks accuracy, making it difficult to meet the energy efficiency ratio standard. In terms of intelligence, air conditioning systems need to monitor current in real time to enable fault prediction and dynamic adjustment. However, sensors/current transformers have slow response times and cannot meet these requirements. Newer refrigerants such as R32 and R290 require even higher accuracy in compressor current monitoring. CHIPSENSE current sensors will offer a good choice for customers.

In modern air conditioning systems, current monitoring has long surpassed the simple function of "overload protection." It has become a key technology for achieving efficient operation, precise control, intelligent diagnosis, and adapting to new challenges.
1. Compressor Current Monitoring: From Protection to Status Awareness
The compressor is the "heart" of an air conditioner, and its current monitoring technology has the most stringent requirements.
Technical Requirements:
High Precision and Dynamic Response:
The Main Reasons Requirement: The compressor load changes with operating conditions (evaporation/condensation temperature), and the current value is the most direct reflection of this load. High-precision monitoring (typically with an error <1%) is required to accurately calculate power and energy efficiency. Simultaneously, rapid response to load surges is necessary to prevent false alarms caused by inrush current.
Implementation Solution: Use a closed-loop Hall effect current sensor or a high-precision sampling resistor + isolated operational amplifier circuit, providing a sufficiently fast response time (<1μs) and bandwidth (>100kHz).It could consider using a CHIPSENSE closed-loop Hall effect current sensor .
Reliable Electrical Isolation and Safety:
Reason for Requirement: The compressor drive voltage is high (380V/220V), requiring the monitoring circuit to be reliably isolated from the main circuit's high voltage to protect the low-voltage control board and personnel.
Solution: Hall effect sensors and current transformers inherently possess isolation characteristics. Sampling resistor solutions require the use of isolation operational amplifiers or linear optocouplers.
Wide Dynamic Range Measurement Capability:
Reason for Requirement: Variable frequency compressors have a wide speed range, with current varying from a few amperes under light load to tens of amperes under full load or startup. The sensor must maintain good linearity throughout this range.
Solution: Select a sensor with a sufficient range (e.g., 0-50A) and high linearity.
2. Current Monitoring in Variable Frequency Control Systems: The Core of Precise Control
In variable frequency air conditioners (especially DC variable frequency air conditioners using permanent magnet synchronous motors), current monitoring is the cornerstone of vector control algorithms.
Technical Requirements:
Ultra-high real-time performance and multi-channel synchronous sampling:
Reason for the requirement: Vector control requires real-time and accurate acquisition of two phases of the compressor's three-phase current (the third phase can be calculated) to decouple the control motor's magnetic field and torque. Sampling delays or asynchrony between channels can lead to control distortion, torque fluctuations, reduced efficiency, and noise.
Implementation Solution: Utilizing multiple high-performance Hall current sensors in conjunction with a high-sampling-rate synchronous sampling ADC in the MCU.
Extremely low phase delay and high bandwidth:
Reason for requirement: The stability of control loops (current loop, speed loop) requires extremely low feedback signal phase delay. Especially under high-frequency switching (such as 20kHz PWM), the sensor must have a bandwidth much higher than the PWM frequency to accurately reproduce the current waveform.
Implementation Solution: A closed-loop Hall current sensor is the preferred choice, with a bandwidth typically exceeding 200kHz and minimal phase delay.
DC Bus Current Monitoring:
Reason for Requirement: Used to reconstruct three-phase current (under a specific modulation algorithm), perform over-current protection, and calculate the total system input power.
Implementation Solution: Connect a Hall current sensor in series at the negative terminal of the DC bus or use a dedicated shunt + isolation amplifier solution.
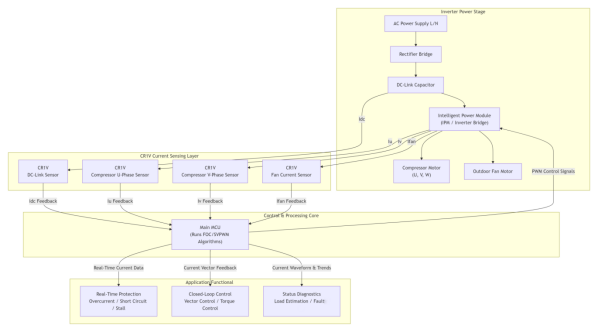
The image above shows a framework diagram of the application of Hall current sensors in air conditioner inverters.
3.Intelligent Fault Diagnosis: From Data to Insight.
Current signals are the "electrocardiogram" of a device's health status, and intelligent diagnosis is an advanced application of current monitoring.
Technical Requirements:
High-Frequency Sampling and Waveform Analysis Capabilities:
Reason for Requirement: Many early faults (such as minor bearing wear, rotor bar breakage, and refrigerant leakage) introduce minute distortions or specific harmonic components into the current waveform. These characteristics cannot be detected through simple RMS monitoring.
Implementation Solution: The system must have high-frequency sampling and storage capabilities, enabling it to perform Fast Fourier Transform analysis of current harmonics or analyze the time-domain characteristics of the current.
Trend Recording and Learning Capabilities:
Reason for Requirement: Intelligent diagnostics relies on long-term data. By recording historical current data (such as peak startup current and average operating current), a normal operating baseline is established. When the current trend undergoes a slow but continuous change (such as a slow increase in operating current), it can provide early warning of decreased system efficiency or mechanical wear.
Implementation Solution: Embedded systems or cloud platforms must possess long-term data recording and trend analysis algorithms (such as threshold-based alarms and machine learning models).
Multi-Parameter Correlation Analysis:
Reason for Requirement: A single current value may not be sufficient to determine the root cause of a fault. Correlation analysis between current and parameters such as pressure, temperature, and vibration is required. For example, high current and high exhaust pressure may indicate a clogged condenser; conversely, high current but normal exhaust pressure may indicate mechanical jamming.
Solution: Implement multi-sensor data fusion analysis within a monitoring system or online platform.
4. New Refrigerant Applications: Addressing New Challenges
To meet environmental requirements, the application of new refrigerants (such as R32, R454B, R290, etc.) presents new demands for current monitoring.
Technical Requirements:
Addressing Higher Discharge Pressures and Temperatures:
Reason for Requirement: Some new refrigerants (such as R32) operate at higher pressures, resulting in greater compressor loads and potentially higher peak currents. The system requires more accurate current monitoring to ensure the compressor operates within its safe operating range and avoids overload.
Solution: Calibrate the current protection threshold to ensure the sensor maintains accuracy even at potentially higher current levels.
Safety Monitoring of Flammable Refrigerants (such as R290):
Reason for Requirement: R290 (propane) is flammable. Preventing any conditions that could lead to compressor stall or overheating is crucial. Current monitoring is the first line of defense against motor overload and overheating, requiring extremely high reliability and response speed.
Solution: Employ redundant or higher-safety-level current monitoring solutions to ensure rapid power disconnection even in extreme conditions.
System Optimization and Efficiency Improvement:
Reason for Requirement: The characteristic curves of the new refrigerant system differ from those of the old refrigerant system. Precise current and power monitoring allows for optimization of the variable frequency control algorithm, identifying the optimal energy efficiency point for the new refrigerant system.
Implementation Solution: Utilizing high-precision current and power data, the control model is continuously calibrated and optimized during both the development and operation phases.
CHIPSENSE CR1V Closed-Loop Hall Current Sensor
The CR1V PB00 series is a closed-loop (compensated) current sensor based on the Hall principle, independently developed by CHIPSENSE. It can be used to measure DC, AC, and pulse currents. The raw materials of CHIPSENSE are comply with UL94-V0, exhibiting excellent linearity and accuracy, extremely low temperature drift, and no insertion loss. CHIPSENSE CR1V Current Sensor
conforms to the following standards: IEC60664-1: 2020, IEC61800-5-1: 2022, and IEC62109-1: 2010.
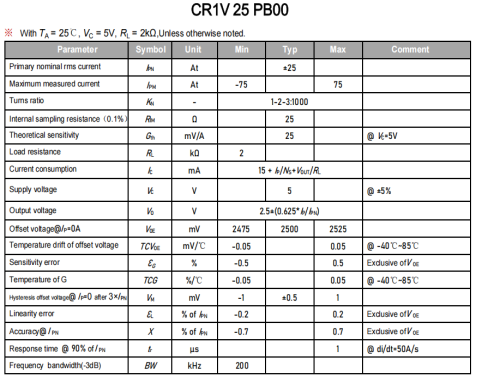
Product parameters (taking CHIPSENSE CR1V PB00 25A current sensor as an example)
Based on the above recommendations for selecting air conditioning system current monitoring systems
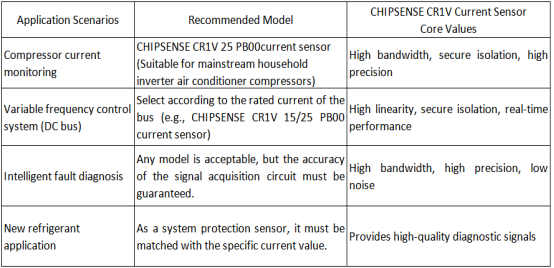
Key selection parameters:
Please select the specific model (CHIPSENSE CR1V 6/15/25 PB00 current sensor) based on the maximum continuous current and peak current measured in the system. For example, a compressor with a rated current of approximately 10A may have a peak current of 20-30A, in which case CR1V 25 PB00 current sensor of CHIPSENSE (rated ±25A, peak ±75A) would be more suitable.
Its typical application diagram:
Conclusion
The demand for current monitoring technology in air conditioning systems is evolving towards higher precision, faster speed, more intelligent analysis, and higher reliability. It has transformed from a passive protection method into a proactive control core and a key enabling technology for predictive maintenance, making it crucial for air conditioning systems to adapt to the trends of high efficiency, environmental protection, and intelligence. CHIPSENSE current sensors will also adapt and upgrade to meet the needs of the times.
CHIPSENSE is a national high-tech enterprise that focuses on the research and development, production, and application of high-end current and voltage sensors, as well as forward research on sensor chips and cutting-edge sensor technologies. CHIPSENSE is committed to providing customers with independently developed sensors, as well as diversified customized products and solutions.
“CHIPSENSE, sensing a better world!
www.chipsense.net
4F, Building C, ZHENGLING.Hi-TECH PARK(Core Space) , No. 2 Cuizhu 2nd Street, Xiangzhou District, Zhuhai, Guangdong Province, China
+86-756-8600806