
Recently, two significant events occurred in my country's new energy construction system. On November 18th, the Concentrated Solar Power Branch of the China Electricity Council was established, and on December 15th, the National Development and Reform Commission and the National Energy Administration jointly issued the "Opinions on Promoting the Scaled Development of Concentrated Solar Power Generation." The former plays an irreplaceable role in promoting standardization and improving the engineering development level of the concentrated solar power industry, while the latter provides industry guidance. The "Opinions" emphasize that concentrated solar power generation should not only reach a certain scale (striving to reach a total installed capacity of approximately 15 million kilowatts by 2030), but also play a supporting and regulating role in the new power system. Concentrated solar power plants are to be operated as power sources that are "dispatchable, measurable, and subject to market settlement." This regulatory capability is essentially the dynamic control capability of the electrical system. CHIPSENSE current sensor is a part of them.
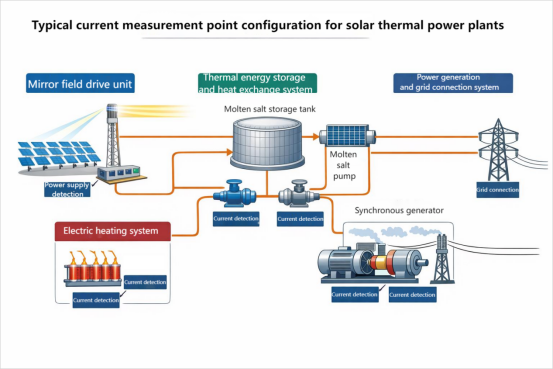
How is the "regulation capability" of a concentrated solar power plant achieved?
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) is a clean energy technology that converts solar energy into thermal energy through concentrating techniques, and then uses this thermal energy to drive a turbine to generate electricity. The current sensor is also one of the important components. The core principle involves using mirrors or lenses to focus sunlight onto a receiver, heating a heat transfer medium (such as molten salt or thermal oil), generating high-temperature, high-pressure steam to drive a turbine, and ultimately powering a generator to produce electricity. From an engineering perspective, a CSP power plant can be broken down into four typical electrical subsystems that work together to achieve its control capabilities:
1.Mirror field system
The mirror field system, also known as the heliostat field or reflector field, primarily functions to collect and focus solar radiation energy, concentrating it onto a receiver (heat absorber) to heat the working fluid (such as molten salt, water/steam, or heat transfer oil), which then drives a turbine to generate electricity. Its main components include:
Reflectors (Mirrors)
Typically, high-reflectivity silvered or aluminized glass mirrors are used.
The shape varies depending on the type of CSP technology:
• Trough systems: Use parabolic trough-shaped mirrors.
• Tower systems: Use flat or slightly concave heliostats.
• Fresnel systems: Use approximately flat, elongated mirrors.
• Dish systems: Use rotating parabolic mirrors.
Support Structure
Fixed or adjustable brackets used to mount and position the mirrors.
Tracking System
Through motors, gear reducers, and a control system, the mirror tracks the sun's position in real time, ensuring maximum solar energy focusing efficiency.
Control System
A central control unit coordinates the movement of thousands of mirrors, precisely aligning them with the receiver.
Includes modules for solar position algorithms, communication networks, and fault diagnosis.
Site Layout and Optical Design
The mirror field layout needs to be optimized to reduce shadowing and blocking losses.
Common layouts include: radial staggered, spiral, and checkerboard patterns.
The characteristics of the mirror field system's operation include a large number of loads, dispersed current levels, and frequent changes in operating status.
2.Thermal Energy Storage and Heat Exchange System
One of the core advantages of concentrated solar power (CSP) generation is its ability to integrate a thermal energy storage system, thereby achieving stable and dispatchable power output, overcoming the shortcomings of intermittent renewable energy sources such as photovoltaic and wind power. The thermal energy storage and heat exchange system is a key technological component for CSP power plants to achieve "daytime heat storage, nighttime power generation" or "peak shaving and valley filling." This part directly determines the peak shaving depth and response speed of the solar thermal system, and is also the area where current surges and continuous high loads coexist. CHIPSENSE current sensor will be used in this field.
Thermal Energy Storage (TES) System
The high-temperature thermal energy generated by the concentrating mirror field is transferred to the heat storage medium through a heat transfer fluid (HTF), and stored in the form of sensible heat, latent heat, or thermochemical energy, and released when needed for power generation. Currently, sensible heat storage is the mainstream method, especially the dual-tank molten salt thermal energy storage system.
Heat Transfer System
The heat transfer system is responsible for efficiently transferring heat between the mirror field, the thermal storage system, and the power cycle, serving as a crucial bridge connecting solar thermal collection and power generation.
3. Power Generation and Grid Connection System
The power generation and grid connection system is the key link in converting solar energy into electrical energy and safely and stably connecting it to the power grid. Compared to fluctuating power sources such as photovoltaics, CSP (Concentrated Solar Power) has stronger dispatchability and grid support capabilities in the power system due to its thermal storage capacity and synchronous generator characteristics. The frequency regulation, inertia response, and black start capabilities mentioned in the "Opinions" are all implemented at this level. In this case, CHIPSENSE current sensor would be an excellent choice.
Power Generation System Components
The power generation section of a CSP power plant is essentially a thermal power generation system, the core of which includes:
1. Thermal Power Cycle System
2. Steam Turbine Generator Set
Typically uses a multi-stage reheat steam turbine (high-pressure cylinder + low-pressure cylinder).
Grid Connection System Architecture
CSP power plant grid connection systems must meet national/regional grid specifications (such as requirements analogous to China's "GB/T 19964 Technical Regulations for Photovoltaic Power Plants Connected to the Power System," or guidelines specifically for CSP). CHIPSENSE current sensors are all manufactured in accordance with national requirements.
Typical grid connection structure:
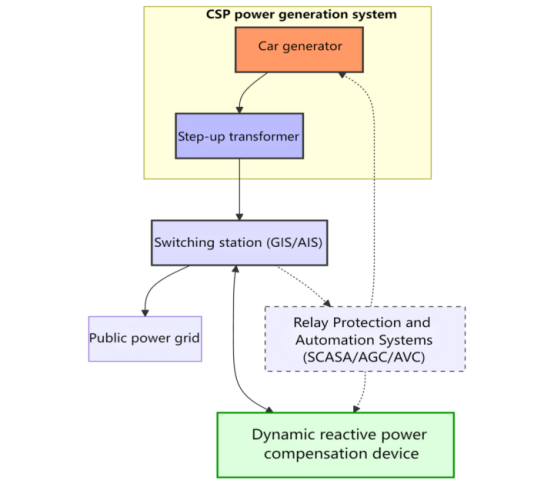
The unique advantages of CSP grid integration (vs. PV/wind power):
In power grids with a high proportion of renewable energy, CSP is considered a high-quality regulating power source and system stabilizer. CHIPSENSE current sensor is used in this.
4. Source-Grid-Load-Storage Coordination Interface
Due to its dispatchability, rotational inertia, and thermal energy storage capabilities, concentrated solar power (CSP) inherently possesses advantages for "source-grid-load-storage coordination" in new power systems. Its "coordination interface" refers to the technical nodes and functional modules that facilitate the interaction of energy flow, information flow, and control flow between the CSP power plant and the power grid, load, other power sources, and energy storage systems. CHIPSENSE current sensors also come in different types.
The realization of the "system value" of concentrated solar power ultimately depends on the highly reliable sensing and control of electrical quantities such as current, voltage, and power.
Adjustable concentrating solar power plants impose system-level requirements on current detection.
At the engineering implementation level, the adjustability ultimately manifests as the dynamic control capability of the electrical system, and current detection is an indispensable fundamental link in this process. Therefore, current sensors have become an indispensable part, and CHIPSENSE current sensors are among them.
1.Dynamic range requirements under wide load operation
Concentrating solar power plants frequently switch between the following operating conditions:
• Abundant heat collection → High-load power generation
• Heat storage and energy release → Nighttime or low-irradiance operation
• Deep peak shaving → Low-load or even near-zero power operation
This requires the current sensing solution to cover a continuous measurement range from small to large currents at the same measurement point, while maintaining linearity and stability.
2.Requirements for response speed under rapid load changes:
When participating in frequency regulation and ancillary services, the system control loop is highly sensitive to:
• Current rise/fall slope
• Sampling delay
• Signal phase lag
Highly sensitive.
The dynamic performance of the detection link will directly limit the upper limit of the regulation performance.
3.Safety and isolation requirements in high-voltage, high-power scenarios:
Typical scenarios in concentrated solar power plants include:
•Generators and excitation systems
•High-power pumps, fans, and electric heating circuits
•Grid connection and plant power systems
Current sensing solutions must meet long-term electrical isolation, safety redundancy, and standard compliance requirements, not just focus on measurement accuracy. CHIPSENSE current sensors are all high-precision.
4.Long Lifespan and Maintenance Friendliness
During a 20–30 year operating cycle:
• High temperature, strong radiation, and dusty environments
• Long-term continuous operation of equipment
• Sensitivity to maintenance costs
This makes power consumption, heat generation, aging drift, and maintainability important factors in the selection process. Many of CHIPSENSE current sensors have also received positive feedback from customers.
Common current detection schemes in solar thermal power plants and their applicable boundaries
In practical engineering, current detection schemes are not a matter of "superiority comparison," but rather a matter of matching the scenario.
1. Shunt resistor scheme
Applicable scenarios:
• Low voltage, low current
• PCB-level current detection
• Highly cost-sensitive and space-constrained applications
CHIPSENSE current sensor meets these requirements.
Engineering Constraints:
• Power consumption and heat generation increase with the square of the current.
• Isolation requires additional design.
• Not suitable for high-power continuous operation circuits.
2. Magnetic Isolation Current Detection (including magnetic core, magnetic modulation, etc.)
Applicable Scenarios:
• Medium to high current
• Requires electrical isolation
• Industrial environment
Engineering Constraints:
• Sensitive to installation location and conductor layout
• Requires consideration of magnetic saturation, temperature drift, and anti-interference design
3. Optical Current Detection Scheme
Applicable Scenarios:
• Extremely high voltage levels
• Strong electromagnetic interference environment
• Grid-side measurement with extreme requirements for isolation distance
Engineering Constraints:
• High cost
• Complex structure
• Requires high levels of maintenance and consistency.
CHIPSENSE current sensors are not only suitable for a wide range of applications but are also easy to install.
Typical Measurement Point Configurations in Concentrated Solar Power Plants from a "Selection" Perspective
In concentrated solar power plants, current measurement typically focuses on the following types of measurement points:
• Mirror field drive and power distribution circuits
Emphasis is placed on quantity, stability, and ease of maintenance.
• Thermal storage and heat exchange system motor circuits
Emphasis is placed on continuous high current capability and thermal stability.
• Electric heating system
Focus is on rapid power regulation and dynamic measurement performance.
• Generator, excitation, and grid connection interface
Priority is given to isolation level, bandwidth, and long-term reliability.
The use of different solutions for different measurement points is itself a reflection of the rationality of the system engineering.
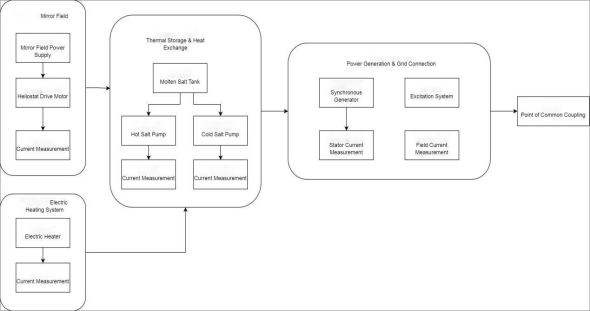
Driven by policy, current sensing is upgrading from a "measurement function" to an "integral component of system capabilities."
Under regulated power supply systems, current sensing is no longer merely used for:
• Display purposes
• Protection purposes
• Single device control
Instead, it directly participates in:
• Regulation capability assessment
• Auxiliary service response
• Market-Oriented Performance Evaluation
In this sense, the selection of the current detection scheme has become part of the system capability design of the concentrated solar power plant, rather than simply a matter of component replacement. Current sensors play an important role here, including the CHIPSENSE current sensor.
Conclusion
The Hidden Engineering Challenges of Scaling Up Concentrated Solar Power
While the scaling up of concentrated solar power generation appears to be primarily a matter of installed capacity, costs, and policies, it fundamentally involves the restructuring of numerous engineering details. Even a small current sensor can play a big role.
Among these, current measurement, as the most basic sensing element, is having its value redefined by the regulated operating mode.
In the new power system, whether a system can be "dispatched, evaluated, and trusted" often depends on seemingly insignificant engineering choices. CHIPSENSE current sensors will be the preferred choice for many customers.
CHIPSENSE is a national high-tech enterprise that focuses on the research and development, production, and application of high-end current and voltage sensors, as well as forward research on sensor chips and cutting-edge sensor technologies. CHIPSENSE is committed to providing customers with independently developed sensors, as well as diversified customized products and solutions.
“CHIPSENSE, sensing a better world!
www.chipsense.net
4F, Building C, ZHENGLING.Hi-TECH PARK(Core Space) , No. 2 Cuizhu 2nd Street, Xiangzhou District, Zhuhai, Guangdong Province, China
+86-756-8600806