
In recent years, with the rapid rise of new energy vehicles, the number of industrial and commercial charging stations has experienced rapid growth.
Whether it's electric trucks in logistics parks, corporate commuter vehicles, or distributed energy systems integrating solar energy storage and charging, charging speed impacts the efficiency and user experience of electric vehicle users. High-power DC fast charging is gradually becoming standard. This brings with it higher requirements for current monitoring accuracy, response speed, and system security. CHIPSENSE is also developing products that adapt to the changes of the times.

Charging piles are divided into AC charging piles and DC charging piles. The former is also called "slow charging" and the latter is also called "fast charging". The technical principle of DC charging piles is to directly connect to the 380V AC power grid and output adjustable DC power to the electric vehicle power battery through the rectifier module, eliminating the conversion step of the on-board charger (See the figure below).
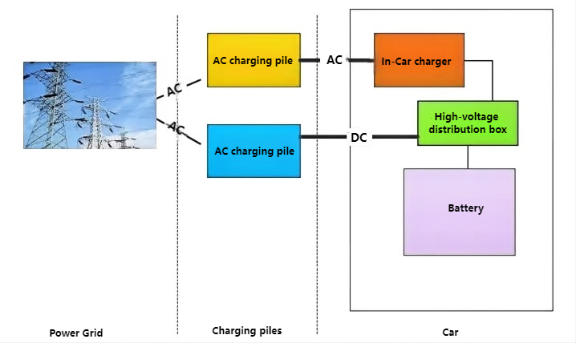
Electric vehicle charging structure diagram
DC fast charging core components:
A DC charging station is a complex system consisting mainly of the following parts:
1. Control Unit
As the core component of a DC charging station, it coordinates and manages the charging process.
Functions include: communication protocol processing (such as GB/T 27930), charging parameter setting, and status monitoring.
2. Charging Module (Power Module)
Converts AC power into a stable DC output.
Usually, it adopts a modular design, with each module providing a certain power output. Multiple modules can be connected in parallel to achieve even greater power output.
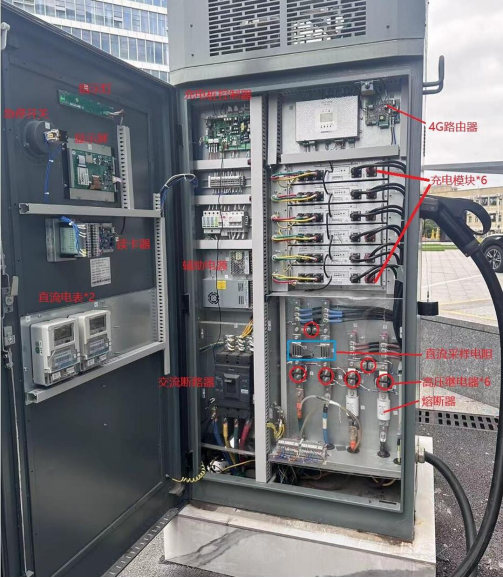

3. Communication Interface
Enables communication with vehicles, the power grid, and backend management systems.Supported protocols include GB/T 27930, OCPP, etc.
4. Human-Machine Interface (HMI)
This includes a display, buttons, or touch panel for user operation and information display.
Some devices support mobile app interaction.
Safety protection devices include over-current protection, short circuit protection, and insulation monitoring to ensure a safe charging process.
6. Housing and Connectors
The housing must meet water and dustproof requirements (typically IP54 or higher).
The connector must comply with standard specifications, such as the GB/T charging interface.
Selection of current sensors in the core components of industrial and commercial DC fast charging piles:
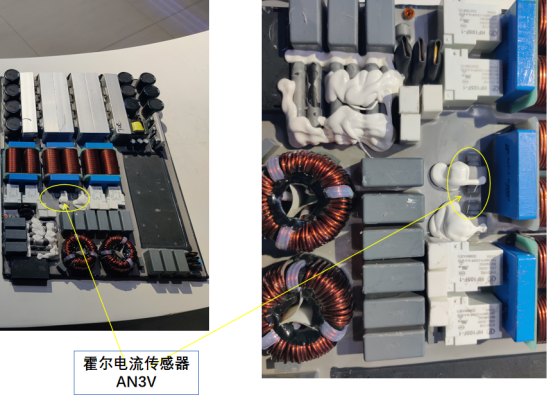
A current sensor with insufficient bandwidth, slow response, or large drift can directly lead to power control lag, anomaly detection failure, and even false triggering of fault protection. Furthermore, due to limited space, DC charging piles typically require compact Hall-effect current sensors.
Currently, the CHIPSENSE AN3V series Hall-effect open-loop current sensors meet these requirements. Recommended models are as follows:
Rectifier unit (AC/DC module)
The rectifier unit converts AC power from the grid into DC power. CHIPSENSE AN3V current sensor can be used to sample the output of the current sampling board outside the rectifier module. Its primary function is to monitor the module's circuit output for abnormalities in real time, as well as to control current sharing and provide protection when modules are connected in parallel. The recommended models are the AN3V 100 PB35 or AN3V 150 PB35 current sensor from CHIPSENSE.
DC/DC conversion module (charging module)
In the DC/DC converter module, the bus voltage is converted to the required charging voltage/current (e.g., 200-750V) for the vehicle. CHIPSENSE AN3V current sensor can be deployed on the output side of the module's current control board/inverter controller interface to provide real-time output current feedback to the main control board, which then uses PWM modulation to control output power. Recommended models: CHIPSENSE AN3V 150 PB35 and AN3V 200 PB35 current sensor.
3. Main Controller (MCU)
The main controller plays a core role in EV charging stations, responsible for coordinating, managing, and monitoring the entire charging process. This includes coordinating power scheduling and managing safety policies across the entire station. It connects to CHIPSENSE AN3V current sensor via the analog sampling interface (ADC) input to form an isolated sampling link, aggregates current values from each power module/output branch, and controls the linkage of devices such as fans and contactors.
4. Charging Gun Control Board (Muzzle Unit)
This control board primarily monitors the vehicle's charging status and controls the gun's relay. An AN3V 80/120 PB35 connector can be soldered and installed on the outside of the gun control board/interface board. This board determines whether the vehicle is fully charged, detects over-current, and, in some V2G-capable systems, monitors the feedback current.
5. Main Contactor & DC Relay Assembly
These components are primarily used to control the on/off switching of current, ensuring a safe and efficient charging process. CHIPSENSE AN3V100 PB35 current sensor can be installed in series with a monitoring point at the contactor outlet in the HVDC distribution unit to determine whether the contactor is loaded when closed, as well as to detect adhesion and arcing faults, thereby protecting the circuit. CHIPSENSE attaches great importance to this.
AN3V application circuit
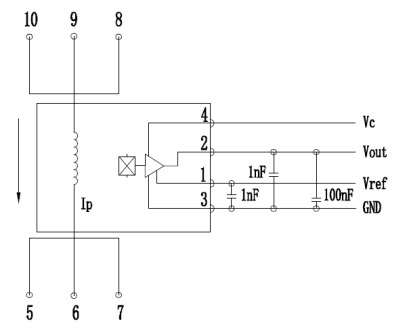
Introduction to CHIPSENSE AN3V current sensor
The new CHIPSENSE AN3V series current sensor, a fully upgraded series of open-loop Hall-effect current sensors from CHIPSENSE, is designed to meet the high-reliability and high-consistency current measurement requirements of power supplies, photovoltaics, energy storage, and other fields. This series not only inherits the advantages of previous generations but also features upgrades and optimizations in materials, structure, and design. These products of CHIPSENSE offer a highly cost-effective alternative to domestically produced products.
The new AN3V series current sensor from CHIPSENSE includes multiple models, including the AN3V PB35/PB55 current sensor, covering a rated measurement range from 80A to 200A. These products not only guarantee measurement accuracy but also significantly increase the dynamic measurement range, enhance reliability, and achieve excellent linearity.
CHIPSENSE is a national high-tech enterprise that focuses on the research and development, production, and application of high-end current and voltage sensors, as well as forward research on sensor chips and cutting-edge sensor technologies. CHIPSENSE is committed to providing customers with independently developed sensors, as well as diversified customized products and solutions.
“CHIPSENSE, sensing a better world!
www.chipsense.net
4F, Building C, ZHENGLING.Hi-TECH PARK(Core Space) , No. 2 Cuizhu 2nd Street, Xiangzhou District, Zhuhai, Guangdong Province, China
+86-756-8600806